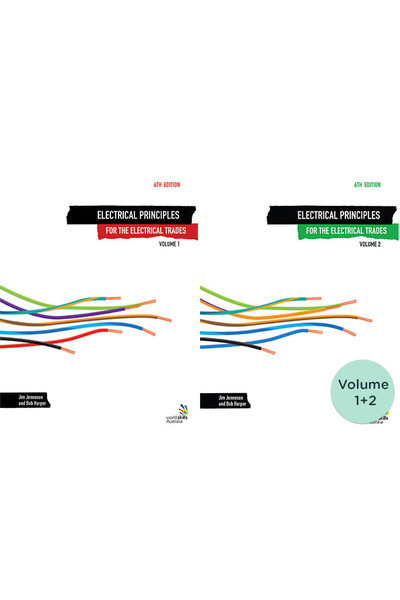
Electrical Principles for the Electrical Trades 6th Edition - Volumes 1 + 2: Blended Learning Package
Part of the series Electrical Principles for the Electrical Trades 6th Edition.
View all products in this series
Electrical Principles for the Electrical Trades is now enhanced with McGraw-Hill Education's unique Connect and Connect Plus to provide a complete blended learning solution for Electrical students. This volume presents knowledge and skills specified in units of competency in national training packages for an electrical trade qualification and advanced trade competencies. Taking on a more practical approach, Electrical Principles for the Electrical Trades now provides students with a range of additional online materials that goes beyond the one-dimensional user experience. This volume is an ideal learning resource for students and trade professionals willing to keep abreast of new developments in Electrotechnology. Electrical Principles for the Electrical Trades 6th Edition provides a logical learning pathway for Certificate II and III in Electrotechnology in the UEE11 Electrotechnology Training Package. These two volumes are the ideal resource for apprentice and non-apprentice trainees as well as practising tradespeople. This text provides students with the fundamental knowledge needed for a career in the electrical trades.
View Competency Grid
Presented in two volumes, Volume 1 covers electrical principles and Volume 2 covers electrical machines. The combination of a clear, simple writing style with full-colour diagrams and photographs make these accessible and engaing to all students and professionals.
Features
- Blended learning and teaching options
- Concise full-colour diagrams and photographs illustrate key concepts
- Appropriate language level for student demographic
- Coverage of Cert II and Cert III Electrotechnology courses mapped to the competencies
- Video animations ensure students can easily engage with examples and readings
- Worksheets, interactive quizzes and testbanks maximise student understanding
- Extensive end-of-chapter summaries and review questions ensure retention of presented theory
- Revised and updated to incorporate relevant competencies in UEE07 Electrotechnology Training Package
- Attractive and engaging new four-colour design
- A wealth of diagrams, photographs, graphs and figures to clearly illustrate key concepts
- Student-friendly writing style demonstrates the logical flow from simple to complex theories
- Revised and updated exercises and examples allow students to assess their understanding of the material
- Appendix material expands on key concepts and creates an authoritative and up-to-date text perfect for VET students and as a reference for trades professionals
- Ideal companion text to Electrical Wiring Practice 7th Edition Volume 1 & Volume 2
Contents
Volume 1
- 1 ELEMENTARY ELECTRICITY
- 1.1 Introduction
- 1.2 Natural electricity
- 1.3 The structure of matter
- 1.4 Static electricity
- 1.5 Dynamic electricity
- 1.6 Potential difference
- 1.7 Electrical materials
- 1.8 Measuring electricity – units
- 1.9 Ohm’s Law
- 1.10 Electrical power and energy
- 1.11 Electrical components
- 1.12 Effects of electricity
- 1.13 Electricity and heat
- 2 ELECTROCHEMISTRY
- 2.1 Introduction
- 2.2 Electrochemical energy sources
- 2.3 Voltaic cells
- 2.4 Electrochemical manufacturing processes
- 2.5 Faraday’s laws
- 2.6 Electrolytic corrosion
- 3 MAGNETISM
- 3.1 Magnetism
- 3.2 Natural magnets
- 3.3 Magnetic characteristics
- 3.4 Electromagnetism
- 3.5 Magnetic units
- 3.6 Magnetisation curves
- 3.7 Magnetic hysteresis
- 3.8 Electromagnetic relay switches
- 4 DC CIRCUITS
- 4.1 Parts of electric circuits
- 4.2 Circuit types
- 4.3 Simple circuit analysis
- 4.4 Series circuit analysis
- 4.5 Parallel circuit analysis
- 4.6 Compound circuit analysis
- 4.7 Circuit analysis
- 5 RESISTORS
- 5.1 Factors affecting resistance
- 5.2 Effects of conductor resistance
- 5.3 Resistor types
- 5.4 Non-linear resistors
- 6 INDUCTORS
- 6.1 Inductors
- 6.2 Generation of an EMF in a magnetic field
- 6.3 Lenz’s Law
- 6.4 Inductance
- 6.5 Inductors in direct current
- 6.6 Inductor types
- 6.7 Applications of inductors
- 6.8 Inductor faults
- 6.9 Testing inductors
- 7 CAPACITORS
- 7.1 Introduction
- 7.2 Capacitance
- 7.3 Capacitors in direct current
- 7.4 Capacitor types
- 7.5 Capacitor faults
- 7.6 Testing capacitors
- 8 SINGLE-PHASE ALTERNATING CURRENT
- 8.1 Introduction
- 8.2 Alternating current generation
- 8.3 Alternators
- 8.4 Parameters that affect the generated EMF
- 8.5 Iron losses in ac generators
- 8.6 Generating sinusoidal waveforms
- 8.7 Voltage and current cycles
- 8.8 Construction of sinusoidal curves
- 8.9 Sinusoidal wave values
- 8.10 Phasors
- 8.11 Harmonics
- 9 ALTERNATING CURRENT CIRCUITS
- 9.1 Introduction
- 9.2 Resistance in ac circuits
- 9.3 Inductance in ac circuits
- 9.4 Capacitors in ac circuits
- 9.5 Series R–L–C circuits on ac current
- 9.6 Parallel R–L–C circuits on ac current
- 9.7 Power in ac circuits
- 9.8 Resonance
- 10 THREE-PHASE ALTERNATING CURRENT
- 10.1 Efficiency in generation and distribution
- 10.2 Power efficiency and number of phases
- 10.3 Two-phase systems
- 10.4 Three-phase systems
- 10.5 Three-phase sine-wave construction
- 10.6 Three-phase connections
- 10.7 Power transmission
- 10.8 Three-phase power
- 10.9 Methods of three-phase power measurement
- 10.10 Volt-Ampere Reactive (VAR) measurement
- 11 CELLS AND BATTERIES
- 11.1 Cell and battery construction
- 11.2 Cell and battery parameters
- 11.3 Safety precautions
- 11.4 Battery maintenance
- 11.5 Primary cells and batteries
- 11.6 Secondary cells and batteries
- 11.7 Fuel cells
- 11.8 Solar, standby power supplies and UPS
- AUXILIARY CHAPTER: TOOLS AND RESOURCES
- T&R.1 Mathematics, numbers and units
- T&R.2 SI units (Système Internationale d’Unités)
- T&R.2.1 Base units
- T&R.3 SI derived units
- T&R.4 Transposition
- T&R.5 Energy, work and power
- T&R.6 Scalar and vector quantities
- T&R.7 Trigonometry
Volume 2
- 1 ELECTROMAGNETIC FORCE
- 1.1 Electromagnetic force
- 1.2 Magnetic circuits
- 1.3 Solenoids
- 1.4 Electromagnet applications
- 1.5 Relays and contactors
- 2 TRANSFORMERS
- 2.1 Operating principle
- 2.2 Transformation ratios
- 2.3 Transformer losses
- 2.4 Transformer construction
- 2.5 Transformer ratings
- 2.6 Transformer cooling
- 2.7 Winding polarities
- 2.8 Parallel connection of transformers
- 2.9 Special transformers
- 3 ELECTRIC MACHINES
- 3.1 Mechanics of electric machines
- 3.2 Terminals
- 3.3 Noise abatement
- 3.4 disassembly—reassembly
- 3.5 Mechanical efficiency
- 4 DC MACHINES
- 4.1 Construction
- 4.2 Commutation
- 4.3 Armature reaction
- 4.4 DC generators
- 4.5 DC Motors
- 4.6 Effi ciency of DC machines
- 4.7 DC servo-motors
- 4.8 DC stepper motors
- 4.9 BLDC motors
- 4.10 Electronically commutated motors (ECM)
- 5 3Ø MOTORS
- 5.1 Construction
- 5.2 Linear motors
- 5.3 Rotating fields
- 5.4 Induction and rotors
- 5.5 Rotor types
- 5.6 Abnormal operating conditions for three-phase motors
- 5.7 Fault diagnosis in 3Ø Motors
- 5.8 Speed/load/torque
- 5.9 Abnormal operating conditions ofthree- phase motors
- 5.10 Diagnosis of faults
- 6 SINGLE-PHASE MOTORS
- 6.1 Operating principles
- 6.2 Induction and its effects
- 6.3 Operating characteristics
- 6.4 Single-phase induction motors
- 6.5 Summary of ac-motors (table)
- 6.6 Comparison of single-phase and three-phase motors
- 6.7 Abnormal operating conditions for ac-motors
- 6.8 Alternating current motor starter circuits
- 6.9 Motor maintenance
- 6.10 Summary Comparison of single-phase motors
- 7 SYNCHRONOUS MACHINES
- 7.1 Three-phase alternator construction
- 7.2 Parallel operation of alternators: synchronising
- 7.3 Standby power supplies
- 7.4 Three-phase synchronous motors
- 7.5 Single-phase synchronous motors
- 8 ELECTRIC MOTOR CONTROL
- 8.0 Motor starters
- 8.1 Three-phase motor reversal
- 8.2 Three-phase motor braking
- 8.3 Three-phase motor starters
- 8.4 Speed control of a.c. induction motors
- 8.5 Alternating current motor protection
- 8.6 Starting principles of direct current motors
- 8.7 Direct current motor reversal
- 8.8 Direct current motor braking
- 8.9 Speed control of d.c. motors
- 8.10 Direct current motor protection
- 8.11 Basic concepts of static and logic control
- 9 ELECTRIC MOTOR PROTECTION
- 9.1 Motor protection
- 10 POWER CONTROL DEVICES
- 10.1 Power control methods
- 10.2 Silicon controlled rectifiers
- 10.3 Gate turn-off (GTO) thyristor
- 10.4 Triacs
- 10.5 Unijunction transistors (UJT)
- 10.6 Programmable unijunction transistor
- 10.7 Diacs
- 10.8 Thyristor phase control
- 10.9 Trigger circuit isolation
- 10.10 Alternating current load control with triacs
- 10.11 Alternating current load control with SCRs
- 10.12 Zero voltage switching
- 10.13 Solid state relays (SSRs)
- 10.14 Fault finding in thysristor circuits
- 11 TEST EQUIPMENT
- 11.1 Circuit indicators
- 11.2 Non-contact testing equipment
- 11.3 Analogue instruments
- 11.4 Digital instruments
- 11.5 Voltmeters
- 11.6 Ammeters
- 11.7 Resistance meters
- 11.8 Analogue multimeters
- 11.9 Digital multimeters
- 11.10 Power and energy meters
- 11.11 Oscilloscope
- 11.12 Use, selection and care of instruments
- 12 ELECTRICAL DRAWINGS AND CIRCUIT DEVELOPMENT
- 12.1 Circuit diagrams
- 12.2 Conventions in line work
- 12.3 Symbols used in electrical circuit diagrams
- 12.4 Placement of circuit components
- 12.5 Drawing schematic circuit diagrams
- 12.6 Other circuit representations
- 12.7 Contactors and relays
- 12.8 Control circuit variations
View Sample Chapters
Also Available
Electrical Wiring Practice
Electrical Wiring Practice presents the knowledge and skills specified in units of competency in national training packages for an electrical trade qualification and advanced trade competencies.
View Electrical Wiring Practice
| ISBN | 9781743075494 |
| Publisher | McGraw-Hill Education |
| Product Type | Student Books, Bundles & Packs, |
| Year Level | VET, |
Be The First To Review This Product!
Help other Teacher Superstore users shop smarter by writing reviews for products you have purchased.